Emergence of Niche Platforms in the Evolving Social Media Landscape
The rapid evolution of social media has shifted user behavior in significant ways, leading to a growing preference for niche platforms over traditional, broad-based networks like Facebook and Twitter. As users become more discerning about their online interactions, the demand for platforms that cater to specific interests, hobbies, and communities has surged. This trend reflects a larger cultural movement towards personalization and hyper-targeted content. Rather than participating in generalized social media experiences, users now seek more focused environments that align closely with their values, preferences, and passions.
The emergence of niche platforms is not only a response to user demand but also a direct challenge to the dominance of the social media giants that have long shaped the digital landscape. Platforms like Twitter and Facebook, which initially catered to broad audiences, are increasingly seen as cluttered and impersonal. While these general-purpose platforms remain popular, their ability to foster meaningful, community-driven interactions has diminished as their user bases have expanded exponentially. The volume of content and the presence of algorithmic-driven feeds have made it difficult for users to find relevant, high-quality interactions. In response, many individuals and groups are migrating to more specialized platforms where the content is curated, and the experience is more tailored to their specific needs.

One of the leading examples of this shift is Discord, a Next-Gen Social platform originally designed for gamers but which has now expanded to host a wide variety of communities ranging from tech enthusiasts to hobbyist groups and educational networks. Discord’s success lies in its ability to offer an environment where users can communicate in real time, share content, and engage in meaningful discussions within a focused context. Unlike larger platforms, where communication is often diffuse and fragmented, Discord offers streamlined, community-oriented spaces, making it easier for users to connect with others who share their interests.

Similarly, Reddit has long thrived by providing a platform where niche communities, known as “subreddits,” can form around virtually any topic imaginable as Next-Gen Social Platforms, From political discourse to specific fandoms and professional industries, Reddit allows users to engage with highly targeted content that reflects their passions and expertise. By utilizing a more democratic approach to content curation, where communities moderate themselves, Reddit has fostered deep, long-term engagement that large platforms like Facebook and Twitter struggle to replicate.

In addition, TikTok, though more mainstream, represents a new form of niche-driven content in the realm of video sharing. While it caters to a wide demographic, the platform’s algorithm is finely tuned to promote highly personalized content, allowing users to dive deeply into specific genres, trends, or subcultures. TikTok’s success is rooted in its ability to engage users with hyper-focused content that aligns closely with their preferences, often leading to niche communities forming around unique topics or even micro-communities within popular trends.
These niche platforms challenge the traditional social media landscape by emphasizing the value of deep engagement over broad reach. As user preferences shift, these platforms provide spaces where individuals can feel more connected, more heard, and more involved with communities that resonate with their values and interests. The ongoing rise of niche platforms suggests a paradigm shift away from the one-size-fits-all model that characterized the early days of social media. Instead, these platforms are shaping the future of digital interaction, offering a more nuanced, personalized approach to online communication.

In conclusion, as users increasingly seek specialized, interest-based experiences, the emergence of niche platforms is not only reshaping the way people interact online but also posing a direct challenge to the once-dominant social media giants. The success of platforms like Discord, Reddit, and TikTok highlights the growing importance of community-driven engagement in the digital age and indicates a shift towards more personalized, focused social media experiences.
· Privacy and Data Protection in Next-Gen Social Platforms: The Shift Toward Secure, User-Centric Platforms
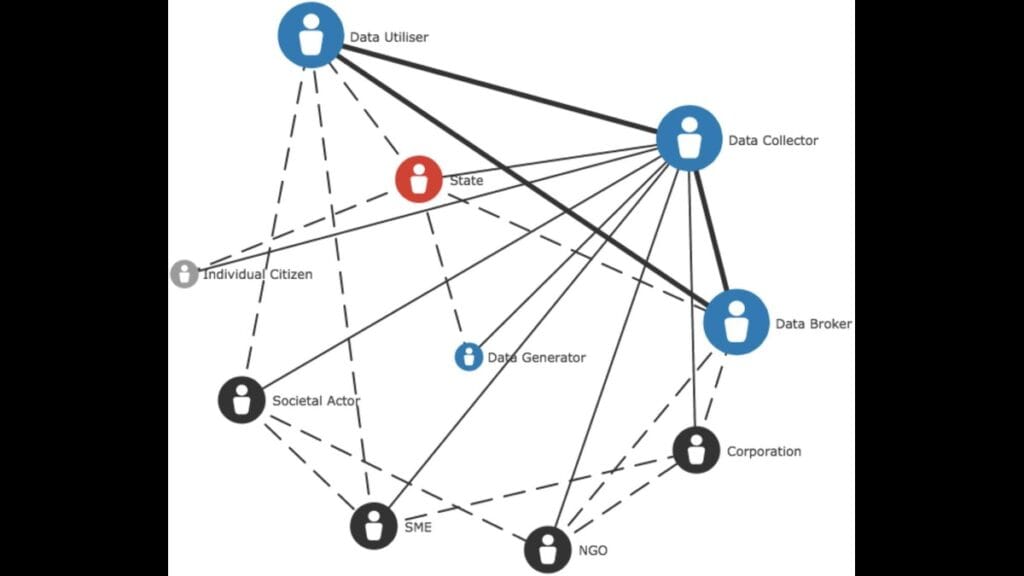
In recent years, the issue of data privacy and security has become one of the most pressing concerns among internet users, prompting a shift away from traditional, centralized social media platforms toward next-generation alternatives that prioritize user autonomy and protection. As data breaches, surveillance practices, and questionable data handling policies continue to make headlines, users are becoming increasingly aware of the risks associated with using legacy platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, which are built on models that capitalize on user data for profit. In response, the demand for platforms that prioritize privacy, transparency, and user control is growing rapidly. This shift is not just a fleeting trend but a fundamental rethinking of how social media should operate in a digital age increasingly defined by concerns over surveillance, data exploitation, and corporate control.
Traditional social media platforms have long been criticized for their opaque data collection practices, which often occur without the full consent or awareness of users. These platforms thrive on the aggregation and monetization of personal data, with algorithms designed to track user behavior, preferences, and interactions to maximize engagement—and, ultimately, profits. As users become more cognizant of the scale and scope of data harvesting, many are choosing to abandon or limit their use of these platforms, seeking alternatives that offer stronger data protections and greater transparency.

One of the most significant changes in the landscape of social media is the rise of next-gen platforms that place privacy and user control at the forefront of their design. These platforms emphasize decentralization and enhanced privacy features, positioning themselves as trustworthy alternatives to corporate-driven models. Mastodon, for instance, is a decentralized social network that operates through a federation of independently run servers, allowing users to choose servers based on their interests or values. This decentralized structure means that no single entity controls the platform, thereby reducing the risks of data monopolization or surveillance by large corporations. Mastodon’s commitment to user privacy is further exemplified by its ad-free model and its emphasis on user autonomy, ensuring that personal data is not harvested or exploited for commercial gain.
Similarly, Signal, an encrypted messaging app, has gained significant popularity for its emphasis on end-to-end encryption and its commitment to not storing any user data. Unlike platforms like Facebook Messenger or WhatsApp, which are owned by larger corporations and subject to varying levels of data-sharing policies, Signal’s open-source nature ensures that its code can be reviewed by security experts, making it a trusted tool for those concerned about data security. By adhering to principles of minimal data collection and user anonymity, Signal has garnered a loyal following among privacy-conscious users.
In addition to these platforms, there has been a significant push for greater regulation and control over data privacy. Movements advocating for user data sovereignty and stronger privacy rights are gaining momentum worldwide, with governments and policymakers introducing new frameworks like the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which gives users more control over their personal information. These regulations, coupled with the rise of privacy-focused platforms, represent a turning point in the digital era, where users are increasingly seeking platforms that align with their privacy expectations and ethical standards.
Moreover, the use of blockchain technology is becoming a key feature in the development of next-gen social media platforms. Blockchain offers a decentralized and transparent approach to data management, ensuring that user data is securely stored and less vulnerable to misuse or centralization. Platforms built on blockchain can empower users to own their data, control how it is shared, and even monetize it if they choose to do so. This shift towards decentralized technologies is likely to play a pivotal role in reshaping the future of social media, offering users more security and control over their personal information.
In conclusion, privacy and data protection have emerged as central pillars of the next generation of social media. As users become more aware of the risks associated with centralized platforms that exploit their data for profit, they are increasingly gravitating toward alternatives that emphasize privacy, security, and user control. Platforms like Mastodon, Signal, and those leveraging blockchain technology represent a paradigm shift in how social media can operate—fostering trust, empowering users, and setting new standards for privacy in the digital age. As the demand for data protection intensifies, it is clear that the future of social media lies in platforms that value and safeguard user privacy.

- Decentralization and Blockchain as Next-Gen Social Platforms: A New Era of User Empowerment in Social Media
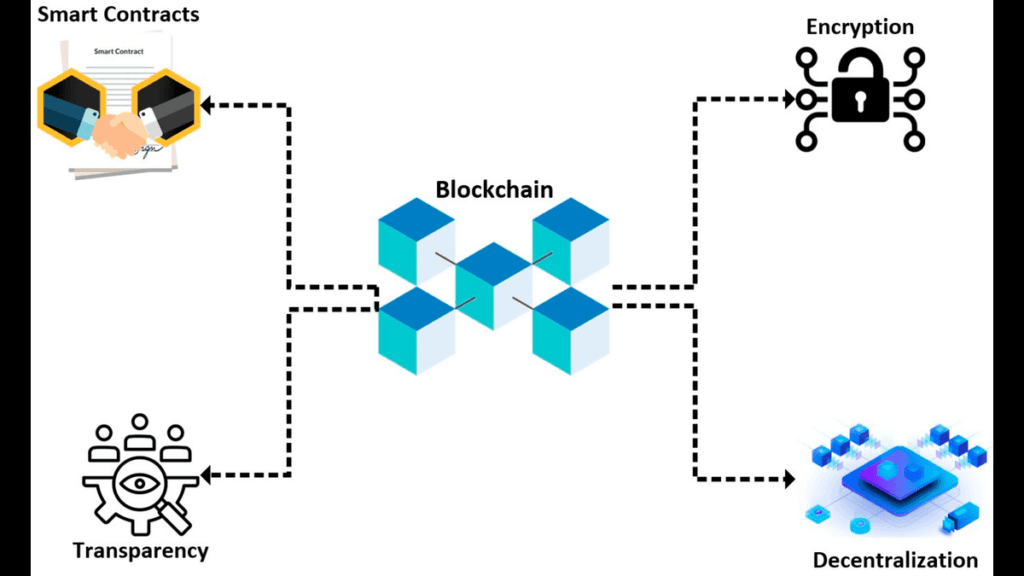
The rise of decentralized technologies and blockchain has emerged as a transformative force in the landscape of social media. As users become increasingly disillusioned with the centralized control exerted by traditional social media platforms, which are often driven by corporate interests, a shift toward decentralization promises to reshape the future of online interaction. Platforms built on blockchain and decentralized technologies offer a new paradigm that emphasizes user autonomy, transparency, and control over content, signaling a fundamental departure from the traditional, corporate-driven social media models.
At the core of decentralized platforms is the idea of user sovereignty—where individuals have greater control over their data, their content, and even the rules that govern the platform. Traditional social media networks like Facebook and Twitter are owned and operated by centralized corporations that control user data, content moderation policies, and the algorithms that dictate what users see. In contrast, decentralized platforms, often built on blockchain technology, allow for a more democratic and transparent governance structure, where no single entity holds centralized power. These platforms are generally community-driven, with users having a direct say in the policies and decisions that shape the platform’s operation, from content moderation to data usage.
One of the most significant advantages of blockchain-based platforms is transparency. Blockchain operates as a distributed ledger technology, meaning that all transactions—whether they are related to data, content sharing, or user interactions—are publicly recorded on an immutable ledger that can be accessed and verified by anyone. This ensures that the actions taken on these platforms, including content moderation, are transparent and auditable. Users can trace the flow of information and understand how decisions are made, eliminating the opaque, often biased decision-making processes common on centralized platforms. This increased transparency fosters trust between users and the platform, making it less likely for harmful practices such as shadow banning, data manipulation, or censorship to occur without accountability.
Furthermore, decentralized platforms provide users with the ability to own and control their own data, a feature that is becoming increasingly important in an era where personal information is often exploited for commercial gain. On centralized platforms, user data is collected, stored, and monetized by the platform itself, typically without explicit user consent or awareness. Blockchain-based platforms, however, empower users to retain ownership of their data. With blockchain’s ability to create secure, encrypted, and immutable records, users have the option to control how their data is shared, with whom it is shared, and even to monetize their content if they so choose. This shift not only reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized use of personal information but also aligns with the growing demand for data privacy and user consent.
One prominent example of this shift is Mastodon, a decentralized social media network that operates through a federation of independently run servers. Users can join any server that aligns with their values and interests, and each server operates under its own rules and governance model. Mastodon’s decentralized structure allows users to maintain greater control over their own content, as there is no central authority governing all interactions. Other examples of decentralized platforms include Steemit, a blockchain-based blogging and social media platform that rewards users for creating and curating content, and Peepeth, which leverages Ethereum blockchain to provide a decentralized alternative to Twitter.
The use of blockchain also offers incentivization models that reward users for their participation. For example, platforms like Steemit use cryptocurrency tokens as rewards for content creators and curators, providing a financial incentive for users to engage in the platform. This not only helps ensure a more sustainable content creation model but also aligns the incentives of the platform with those of its users, rather than with advertisers or corporate stakeholders. This economic model challenges the traditional ad-based revenue systems that dominate centralized platforms, where the primary focus is to maximize profits by selling user data to third-party advertisers.
Moreover, decentralized platforms reduce the influence of large corporations over content creation and dissemination. On platforms like Facebook and Twitter, content moderation and algorithmic recommendations are often guided by profit-driven motives, which can result in the amplification of sensationalist or polarizing content. Decentralized networks allow communities to establish their own rules and norms around content moderation, providing users with a greater sense of agency over what is deemed acceptable within their communities. This decentralized approach ensures that platforms are less likely to be influenced by the interests of powerful corporate entities or political agendas.
In conclusion, the rise of decentralized and block chain-based platforms is reshaping the social media landscape by offering greater user control, transparency, and data ownership. As users continue to seek alternatives to the traditional, corporate-controlled social media model, decentralized platforms provide a compelling solution that emphasizes privacy, accountability, and community-driven governance. With block chain technology at the forefront of this shift, the future of social media looks poised to embrace a more user-centric, equitable, and transparent approach to online interactions.

- New Forms Next-Gen Social Platforms: The Role of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) in the Future of Social Media
The next wave of social media is being significantly shaped by the integration of immersive technologies, primarily Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR). These technologies are redefining how individuals connect, interact, and engage within digital environments, pushing the boundaries far beyond the traditional text and image-based formats that have long dominated platforms like Facebook and Twitter. As the digital landscape evolves, platforms leveraging VR and AR are transforming social interaction by creating more immersive, interactive, and sensory-rich experiences that mimic real-world engagements while offering new forms of online communication.
One of the most notable developments in this space is Meta’s Horizon Worlds, which exemplifies how VR is reshaping the social media experience. Horizon Worlds, built on the foundation of Meta’s larger Metaverse vision, allows users to immerse themselves in fully virtual worlds where they can interact with others in real-time through avatars. In contrast to the traditional, two-dimensional interactions on social media platforms, Horizon Worlds enables users to explore expansive virtual environments, attend virtual events, create digital content, and engage in meaningful conversations—all within a 3D space. This immersive, avatar-based interaction offers a more lifelike and intuitive form of connection compared to text-based posts or even video calls. Through VR, users can experience a deeper sense of presence, making interactions feel more natural and engaging.
The potential of Virtual Reality (VR) in social media extends far beyond simple chat or content sharing. It allows for entirely new experiences, such as attending virtual concerts, exploring distant places through VR travel experiences, or participating in real-time collaborative environments. For instance, VR can enable users to hold business meetings or participate in educational sessions that replicate physical interaction, fostering an environment conducive to creativity and problem-solving. Such capabilities transform VR from a tool for entertainment into an essential platform for social interaction, learning, and work, creating opportunities for deeper, more authentic connections in an increasingly digital world.
Similarly, Augmented Reality (AR) is playing a crucial role in augmenting real-world experiences with digital elements, thus enhancing social interactions in innovative ways. While VR immerses users in entirely virtual worlds, AR overlays digital objects onto the physical world, allowing users to interact with virtual elements in their immediate environment. Social media platforms, such as Instagram and Snapchat, have already embraced AR through interactive filters and effects, but the future of AR lies in its ability to enhance live, real-time communication. AR-powered interactions could include features like virtual overlays in social gatherings, where users can instantly interact with contextual content—be it art, games, or advertisements—integrated into the real-world surroundings. Additionally, AR could revolutionize shopping, education, entertainment, and collaboration, offering users a highly interactive, customized experience.
As VR and AR technologies mature, they also promise to address many of the shortcomings of traditional social media. For example, traditional social media platforms, such as Facebook and Twitter, have been criticized for fostering superficial interactions where users often communicate in isolated, disconnected ways. While these platforms have allowed for some degree of engagement, they have not fully replicated the richness and complexity of in-person social interactions. VR and AR technologies offer an alternative by providing multisensory, immersive experiences that enable users to feel more present and engaged with others. By utilizing virtual spaces, users can participate in interactive environments that mimic the richness of physical interactions, thus overcoming the barriers of text, images, and even video conferencing.
In addition to improving personal connections, VR and AR technologies offer significant potential for businesses and brands. Companies are increasingly leveraging VR and AR as part of their marketing and customer engagement strategies. Virtual product demonstrations, interactive brand experiences, and immersive advertising can create deeper emotional connections with consumers, setting a new standard for customer engagement that transcends traditional advertising methods. Brands can create dynamic, interactive environments where customers not only view products but experience them in a fully interactive, 3D setting, leading to a more memorable and personalized experience.
Despite the potential, the widespread adoption of VR and AR in social media also faces challenges. The accessibility of VR and AR devices, such as headsets and specialized hardware, remains a significant hurdle, as many users may not have access to the necessary technology. Furthermore, there are concerns regarding user safety, data privacy, and ethical considerations related to immersive digital experiences. As the technology continues to evolve, it will be crucial for platform developers to address these challenges to ensure a safe, inclusive, and responsible use of VR and AR in social media.
In conclusion, VR and AR are poised to redefine the social media landscape by offering new and innovative forms of interaction that go beyond the limitations of traditional platforms. Through immersive, sensory-rich experiences, these technologies enable users to connect on a deeper level, collaborate in real-time, and engage with digital content in ways never before possible. As Meta’s Horizon Worlds and other VR/AR platforms evolve, they will likely become central hubs for social interaction in the digital age, shaping the future of how people communicate, collaborate, and connect in virtual environments.
- Next-Gen Social Platforms: Algorithmic Control vs. User Control
In recent years, social media users have become increasingly disillusioned with the dominance of algorithms in shaping the content they see on platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. These platforms rely heavily on algorithmic models that prioritize content based on engagement metrics, such as likes, shares, and comments, rather than user preferences or interests. While this algorithmic approach has been effective in driving user engagement, it has also led to a variety of criticisms, including the promotion of sensationalist content, echo chambers, and manipulation of users’ emotions and opinions. As a result, there is a growing demand for social media platforms that prioritize user control over algorithm-driven content, signaling a shift toward more personalized, user-curated experiences.
Traditional social media platforms have long been designed to maximize engagement, with algorithms that push content to users based on their past interactions and demographic data. These algorithms determine what users see in their feeds, often promoting content that is designed to elicit strong emotional responses or increase time spent on the platform. While these strategies have been successful in maintaining user engagement, they have also created a number of unintended consequences. For example, by promoting content that sparks controversy or outrage, algorithms can fuel polarization, spreading misinformation and deepening societal divisions. The emphasis on engagement also leads to a preference for viral, attention-grabbing content over more thoughtful or meaningful exchanges.
Another significant issue with algorithmic control is the lack of transparency in how content is filtered and displayed. Users often have little insight into the criteria that determine which posts appear in their feeds or the biases that might shape these decisions. The opacity of these algorithms has led to growing concerns about the manipulation of information, as users are not always aware of how their data is being used or how their content consumption is being influenced by invisible algorithms. This lack of transparency has created a desire for greater autonomy in how users engage with content and control the information they are exposed to.
In response to these challenges, the next generation of social media platforms is placing a strong emphasis on user control over content. These platforms are exploring alternative models that give users more agency in shaping their online experience. For example, instead of relying on an algorithm to determine what users see, some next-gen platforms are focusing on user-curated feeds, where individuals can directly choose which content they want to engage with. This model allows users to follow topics, creators, and communities that align with their interests, without the influence of an algorithm designed to optimize for engagement metrics. By providing more control over the content that appears in their feeds, these platforms aim to foster more intentional, meaningful interactions rather than passive consumption driven by external factors.
User-curated content also allows for a more diverse and personalized experience, as individuals can prioritize content based on their values, preferences, and expertise. For instance, platforms like Mastodon, a decentralized social network, allow users to select servers and communities that align with their interests, offering a more niche and tailored social media experience. Similarly, new social platforms that focus on interest-based curation—where users can select and interact with content based on specific topics, rather than relying on an algorithm to surface content—are gaining traction. This model could lead to a more balanced and authentic form of social media, where users are more engaged with the content they genuinely care about, rather than being driven by the need for viral interaction.
Moreover, some platforms are beginning to introduce features that allow users to have more direct influence over the algorithms themselves. For instance, some social media networks are exploring algorithmic transparency tools, which would enable users to see how algorithms work and adjust them according to their preferences. In these models, users can opt out of algorithmic recommendations entirely, choosing instead to receive content in a chronological or randomized order, which can reduce the feeling of being manipulated by algorithms.
The demand for user control extends beyond content curation and touches on the issue of privacy and data usage as well. Many users are now questioning how much personal data they are willing to share with platforms that rely on algorithms to personalize content. By shifting to user-controlled models, social media platforms can align more closely with evolving privacy standards and build trust with their audiences. Users who feel empowered to control both the content they consume and the data they share are more likely to engage in a positive, long-term relationship with these platforms.
In conclusion, the growing demand for user-curated feeds rather than algorithm-driven content represents a paradigm shift in the social media landscape. By placing more control in the hands of users, next-gen platforms have the potential to foster a healthier, more transparent, and more personalized social media experience. This shift away from algorithmic dominance could mitigate some of the most significant issues facing traditional social media platforms, including the spread of misinformation, the amplification of sensationalism, and the erosion of user trust. As these new platforms evolve, they will likely lead the way in defining the future of online interaction—one that is user-centric, intentional, and more focused on quality over quantity.

- Short-form and Video-based Next-Gen Social Platforms: The Shift Toward Instant, Visual Engagement
The rise of short-form, video-based content has become one of the most dominant trends in the current social media landscape. Platforms like TikTok have redefined how content is consumed and created, offering a fast-paced, visually engaging experience that has captivated users worldwide. In contrast to traditional, text-heavy formats or long-form videos on platforms like YouTube, short-form video emphasizes quick, digestible content that fits seamlessly into the user’s daily routine. This shift toward video-centric platforms has revolutionized social media by reshaping user expectations, consumption patterns, and engagement strategies, and it has forced traditional platforms to rapidly evolve or risk losing relevance.
TikTok’s explosive success has not only transformed social media but also established a new paradigm of content creation and consumption. The platform’s focus on 15 to 60-second videos offers an accessible and highly engaging way for users to interact with content. This brevity, combined with an addictive algorithm that personalizes recommendations based on user behavior, has made TikTok a central hub for viral trends, challenges, and memes. For many users, TikTok has become the primary platform for discovering new music, learning about current events, or watching educational content, all in a highly visual, easily consumable format.
This rise in popularity of short-form video content can be attributed to several factors. First, it aligns perfectly with the decreasing attention spans of internet users, as people seek immediate gratification and prefer quick, entertaining bursts of content. The algorithm-driven feed of platforms like TikTok provides users with a constant stream of fresh content tailored to their tastes, ensuring that engagement remains high. Additionally, the ease of content creation plays a significant role in TikTok’s success. Unlike platforms like YouTube, which often require high production values and professional equipment, TikTok encourages user-generated content with minimal barriers to entry. Users can create and share videos using their smartphones, often leveraging built-in editing tools, filters, and effects to enhance their content. This democratization of content creation has led to an explosion of creativity and a more diverse range of voices, making short-form video a highly influential form of communication.
As short-form video continues to rise in popularity, traditional platforms are being forced to adapt in order to retain users and stay relevant. Instagram, once known primarily for photo sharing, has pivoted to incorporate video-centric features like Reels, which are directly modeled after TikTok’s format. Similarly, YouTube has introduced Shorts, a feature designed to capture the same attention of users seeking quick, vertical videos. Even Facebook has made moves toward integrating more video content, with the platform increasingly prioritizing video in user feeds, particularly live videos and short clips.
However, the success of short-form video content has also raised important questions about the long-term impact of this shift. While it offers users fast entertainment, it also introduces concerns about the quality of content and its effects on the broader social media ecosystem. For example, the focus on viral trends and brief videos can promote superficial content over deeper, more thoughtful engagement, potentially diluting the overall value of social interactions online. Moreover, the rapid consumption of content can lead to information overload, where users are bombarded with stimuli without the time to process or reflect, contributing to cognitive fatigue and the erosion of attention span.

Increased Focus on Mental Health: Addressing the Impact of Social Media on Well-being
Alongside the rapid evolution of content consumption, there has been a growing concern about the mental health impact of social media, which has become an increasingly important issue for both users and platform developers. As social media platforms have become more embedded in daily life, research has increasingly highlighted their potential negative effects on mental health, particularly among young users. The pressure to conform to unrealistic standards of beauty, success, and lifestyle, the constant comparisons fostered by curated posts, and the overwhelming exposure to the best moments of others’ lives have been linked to increased levels of anxiety, depression, and loneliness. This has sparked a conversation about the need for next-generation platforms to adopt a more user-centric approach that prioritizes mental health and well-being.
Social media has often been associated with negative psychological outcomes, including cyberbullying, social comparison, and addiction. Platforms that reward attention-grabbing, highly polished content, such as Instagram or TikTok, contribute to the cultivation of a culture where users feel pressured to present idealized versions of themselves. This leads to a disconnect between online personas and real-life identities, which can create feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem. Moreover, the fear of missing out (FOMO), which is exacerbated by the constant stream of posts about exciting events or achievements, can make users feel disconnected from others or left behind, particularly among younger generations who are more susceptible to peer pressure.
The issue of social media addiction is also of growing concern. The constant notifications, endless scrolling, and the design of platforms to maximize user engagement contribute to compulsive usage patterns. Research shows that excessive time spent on social media can lead to disrupted sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and a decline in real-world well-being. The resulting sense of isolation can be particularly harmful to vulnerable individuals, further amplifying the mental health crisis.
As a response to these challenges, next-gen social media platforms are increasingly prioritizing user well-being. These platforms are exploring a range of features aimed at mitigating the negative impacts of social media use. One key strategy is content moderation designed to reduce toxicity, online bullying, and harassment. Platforms are introducing safe spaces, automated filters, and community guidelines that actively work to protect users from harmful content. For instance, social networks like Instagram have taken steps to reduce cyberbullying by introducing features that allow users to block harmful comments or hide negative posts. Similarly, TikTok has invested in enhancing its content moderation tools to identify and remove toxic content related to hate speech and misinformation.
Another area of focus for next-gen platforms is reducing screen time and promoting healthier habits. Some platforms now offer screen time monitoring tools, allowing users to track and limit their daily usage. Time limits, notifications management, and digital detox features are also being integrated to help users maintain a healthier balance between their online and offline lives. Additionally, the design of these platforms is evolving to encourage meaningful engagement rather than passive consumption. Platforms that emphasize positive reinforcement, supportive communities, and mindful interaction aim to cultivate environments where users can connect over shared interests in a healthy and supportive way.
Furthermore, next-gen platforms are increasingly looking at ways to integrate mental health resources and wellness tools directly into the user experience. For example, Instagram has rolled out a feature that encourages users to take breaks after extended use, while YouTube has added a “Time Watched” feature that gives users insights into how much time they’ve spent on the platform and encourages healthier habits. Similarly, apps like Headspace and Calm are often partnered with social media platforms to offer users tools for relaxation, mindfulness, and stress reduction.
In conclusion, the convergence of short-form, video-based content and the growing concern for mental health represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of social media. While the shift toward quick, engaging video content reflects the changing nature of online interaction, it is equally important that the next generation of platforms acknowledge and address the potential harms associated with excessive social media use. By focusing on mental health and prioritizing user well-being, next-gen platforms have the opportunity to foster healthier online environments that encourage meaningful engagement, support authentic connections, and ultimately lead to a more positive, balanced social media experience.

- AI and Automation in Content Creation: Revolutionizing Next-Gen Social Platforms Interaction
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation into social media platforms is fundamentally altering the landscape of content creation, moderation, and user engagement. As the demand for personalized and dynamic experiences increases, AI-driven tools are becoming indispensable in shaping how users interact with content. From enhancing the creative process to ensuring a safer online environment, AI is transforming the ways in which people both create and consume content. This technological advancement is poised to significantly impact social media platforms, giving rise to new possibilities for content generation and more personalized, user-driven experiences.
In the realm of content creation, AI is empowering users by providing sophisticated tools that streamline and enhance the creative process. AI algorithms are capable of analyzing vast amounts of data to help users generate content that resonates with their audiences. For instance, AI-driven tools can assist in video editing, image enhancement, and even writing by offering automatic suggestions based on trends, audience preferences, or the user’s historical content. Platforms like Instagram and TikTok already utilize AI to offer creative filters, effect generation, and post-scheduling features that enable users to enhance their content with minimal effort. These tools significantly reduce the barriers to high-quality content creation, allowing amateur creators to produce professional-level visuals and narratives without requiring advanced technical skills or equipment.
Furthermore, AI-generated content has expanded beyond editing tools to include the creation of entirely new media. For example, AI-powered algorithms can now generate text, artwork, and even music, blurring the lines between human and machine creativity. Platforms like OpenAI’s GPT are enabling content creators to produce written material efficiently, while other AI tools can generate original music tracks or visual art. This shift allows for an entirely new dimension of content creation, as AI can act as both a co-creator and a tool for inspiration. As the technology evolves, it is likely that AI will play an even more central role in content generation, creating opportunities for personalized storytelling and interactive digital experiences that were previously unimaginable.
On the moderation and engagement front, AI is transforming how platforms manage content and interactions, ensuring that users have a safer and more customized experience. Content moderation is one of the most critical areas in which AI is being applied. Traditional moderation methods often struggle to keep up with the sheer volume of posts, comments, and interactions occurring on major platforms. AI-powered algorithms, however, can analyze text, images, and videos in real-time, automatically flagging inappropriate content such as hate speech, misinformation, or graphic material. These tools significantly reduce the workload of human moderators and improve response times, ensuring that users are exposed to safer environments. Additionally, AI can detect and block bot-generated content and fake accounts, helping to maintain the integrity of online communities.
The use of AI also plays a significant role in personalization. AI algorithms track user behavior, preferences, and engagement patterns to create customized content feeds. By continuously learning from user interactions, these systems can offer tailored experiences that enhance engagement and user satisfaction. This level of personalization goes beyond just suggesting content based on past behavior; AI can predict future interests, optimize ad placements, and even create dynamic content that evolves as users’ tastes change. The personalized experience created by AI can lead to increased time spent on platforms, as users are more likely to engage with content that resonates with them on an individual level.
However, the growing reliance on AI for content creation, moderation, and engagement raises questions about authenticity and control. The fine balance between automation and human input will be crucial in maintaining trust and transparency on social media platforms. While AI offers the promise of efficiency and personalization, there are concerns about the potential for AI to perpetuate bias or manipulate user experiences in ways that are not immediately apparent. The ethical implications of AI-driven content moderation—such as the risk of over-censorship or the stifling of diverse viewpoints—are also significant areas of concern. Moreover, users may become wary of AI-generated content that lacks the personal touch or originality that human creators bring to the table.
In conclusion, the integration of AI and automation into social media platforms is reshaping the digital landscape in profound ways. From enhancing creativity and making content creation more accessible to improving safety and user engagement, AI is driving the evolution of social media. As these technologies continue to advance, they will unlock even more opportunities for interactive, immersive, and personalized experiences that challenge traditional norms of social media interaction. While AI presents immense potential for innovation, it is essential that developers and platforms balance automation with ethical considerations to ensure that the future of social media remains transparent, authentic, and human-centric.
for more update please visit out website:blogifyzones.com


